
 Fundamental Building Blocks Of Cloud Computing
Fundamental Building Blocks Of Cloud Computing
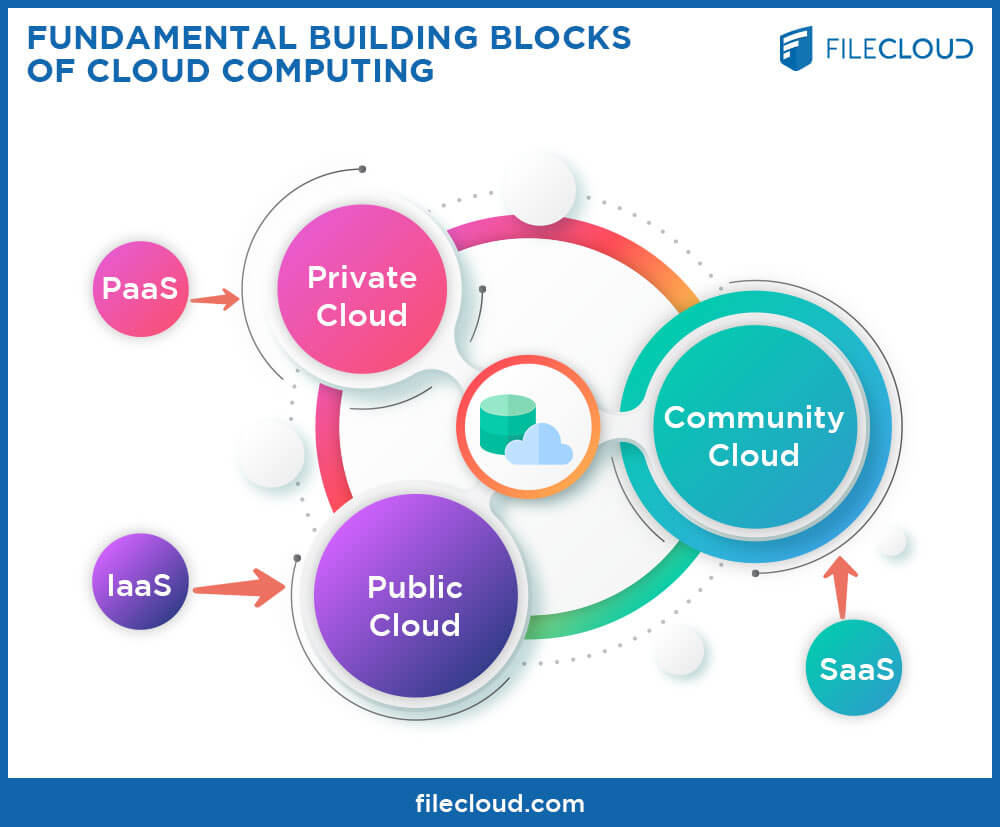
The term 'cloud computing' has reached masses, and rarely we come across an organization that doesn't use or considering cloud. Cloud computing is an extensive term that sums up a wide range of services. Since the cloud is a vast collection of services, enterprises can choose how, when, and where they wish to use cloud computing. There are typically three major offerings that sum up cloud computing services. The three are Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). In most cases, the ‘layers’ of cloud computing are represented as a pyramid with IaaS at the bottom, PaaS at the middle and SaaS sits at the top. Describing and differentiating the three is key to gaining a better understanding of Cloud computing.
SaaS
This is the cloud computing layer most people have interacted with and are likely to use in their day to day lives. Software as a service is where computing applications are accessed through the internet; this eliminates the need to download, install and run applications on local computers. In most cases, these applications are managed by a third party vendor. The user has to log into an account in order to gain access to the applications interface.
A good example of SaaS is Google docs; if you don’t have MS Office installed on your computer, you can use Google docs to create and edit documents. Most SaaS applications are either free to use or require some form of subscription. In order to help you gain a better understanding of SaaS, below is a list of its characteristics and benefits.
SaaS Characteristics
- A ‘one to many’ model is used for software delivery
- Software management is done from a centralized location
- Access to the commercial application is gained via the internet
- The end users need not worry about software patches and upgrades
- Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) enable integration with other application
SaaS Benefits
- Dynamic Scalability
- Device independence
- No fixed costs
- Collaborative- allows multiple sharing of information
- Constant Updates
The main disadvantage of SaaS is that it’s a ‘what you see is what you get’ form of cloud computing and currently, limited to browser capabilities. Another drawback of SaaS is the security concerns that surround it. However, businesses looking for a more customize experience can use cloud at the Infrastructure and Platform level.
PaaS
A platform is a software environment used to develop and run applications. So Platform as a Service (PaaS) can be defined as a computing platform that enables the creation, testing and implementation of software easily and quickly without the complexities of buying and maintaining the infrastructure and additional software. Unlike SaaS which is software delivered via the internet, PaaS provides a platform for creation of applications over the internet. Another difference between PaaS and SaaS is the aspect of management. In PaaS, the vendors manage networking, storage, servers, virtualization, OS, middleware and runtime, but the end users are the ones who manage the data and applications.
 Examples Of PaaS
Examples Of PaaS
Some common examples of PaaS include Google App engine, MS Azure and force.com. Its characteristics are listed below.
PaaS Characteristics
- Has services that allow development, testing, deployment, hosting and maintenance of applications
- Has web based UI design tools that enable the development, modification, testing and deployment of different User Interface scenarios
- The platform can be accessed and utilized by multiple users
- Integration with databases and web services through regular standards
- Development support (Project planning tools)
- Tools that handle subscription and billing management
PaaS Benefits
- Cost reduction
- Streamlined application development and management
- Increased mobility
- Reduced technical maintenance
The main disadvantage of PaaS is its restrictive nature. Despite the fact that it makes the development of online applications easy, developers are restricted to the programming languages and tools provided by the PaaS vendor.
IaaS
The final and most fundamental layer of cloud computing is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS); it is sometimes referred to as Hardware as a Service. In this scenario, computing infrastructure (virtualized environment), networking and storage are delivered over the internet. Instead of heavily investing in the purchase of servers, network equipment and datacenter maintenance; an enterprise can simply purchase these services on demand. A good example of a Public IaaS offering is Amazon Web Services.
Since IaaS is the most fundamental building block, it covers the areas where PaaS and SaaS do not; making it the ideal cloud computing solution. The characteristics of IaaS are listed below.
IaaS characteristics
- Resources and infrastructure are distributed as a service
- Enables dynamic scaling
- Multiple users utilize a single piece of hardware.
The ‘Public Cloud’ consists of resources and infrastructure that is shared amongst several users while the ‘Private Cloud’ is infrastructure that emulates all the features of cloud computing on a private network. For a better understanding of public and private cloud computing, take a look at Public vs. Private Cloud Computing Basics. When it comes to private cloud solutions, good examples include OwnCloud and FileCloud which allows you to effectively manage your private cloud infrastructure.

By Team FileCloud